RAID 10 Data Recovery
RAID 10 Data Recovery – RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, offers a combination of mirroring and striping, providing both redundancy and performance benefits. However, despite its robust architecture, data loss can still occur due to various reasons such as disk failures, controller malfunctions, human errors, or software issues. In this guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of RAID 10 data recovery, offering insights and strategies to help you retrieve your valuable data effectively.
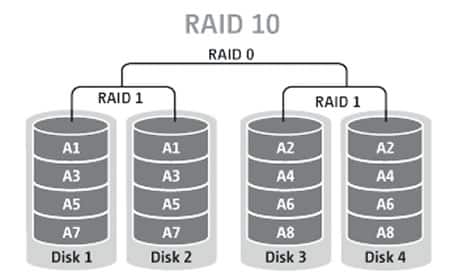
Understanding RAID 10 & it’s Complexity:
RAID 10 combines the features of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping) to provide redundancy and performance improvements simultaneously. In RAID 10, data is mirrored across multiple pairs of drives and then striped across those mirrored sets. This ensures that if one drive fails, the data can still be accessed from its mirrored counterpart, minimizing the risk of data loss.
Common Causes of Data Loss in RAID 10:
- Disk Failures: Individual drive failures can compromise the integrity of RAID 10 arrays.
- Controller Failures: Malfunctions in RAID controller hardware or firmware can disrupt data access.
- Human Errors: Accidental deletion, formatting, or overwriting of data can lead to data loss.
- Software Issues: Corruption of RAID configuration, operating system failures, or software bugs can result in data unavailability.
Steps for RAID 10 Data Recovery:
- Assess the Situation:
- Determine the nature and extent of the data loss.
- Identify the cause of the RAID failure (e.g., disk failure, controller malfunction).
- Safeguard the Drives:
- Ensure that all drives in the RAID array are powered off to prevent further damage.
- Label each drive with its position in the array for easy identification.
- Seek Professional Assistance:
- Contact a reputable data recovery service provider with expertise in RAID systems.
- Provide detailed information about your RAID configuration and the circumstances leading to data loss.
- DIY Data Recovery (Optional):
- If you have the necessary technical skills and tools, you may attempt DIY data recovery.
- Exercise caution to avoid further damage to the drives or loss of data.
- Rebuild the RAID Array:
- Once the data has been recovered, rebuild the RAID array according to the original configuration.
- Replace any faulty drives and reinitialize the RAID set if required.
- Data Verification:
- Verify the integrity of the recovered data to ensure its accuracy and completeness.
- Perform thorough testing to identify any potential issues or inconsistencies.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Backups: Implement a robust backup strategy to mitigate the impact of data loss.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the health of RAID components and perform maintenance tasks as needed.
- RAID Controller Redundancy: Utilize redundant RAID controllers to minimize the risk of controller failures.
- Data Recovery Planning: Develop a comprehensive data recovery plan outlining procedures to follow in the event of data loss.
RAID 10 offers an effective solution for both performance and redundancy in data storage. However, data loss can still occur due to various factors. By understanding the common causes of data loss and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can improve your chances of successful RAID 10 data recovery. Remember to prioritize preventive measures to safeguard your data and minimize the likelihood of future incidents.

